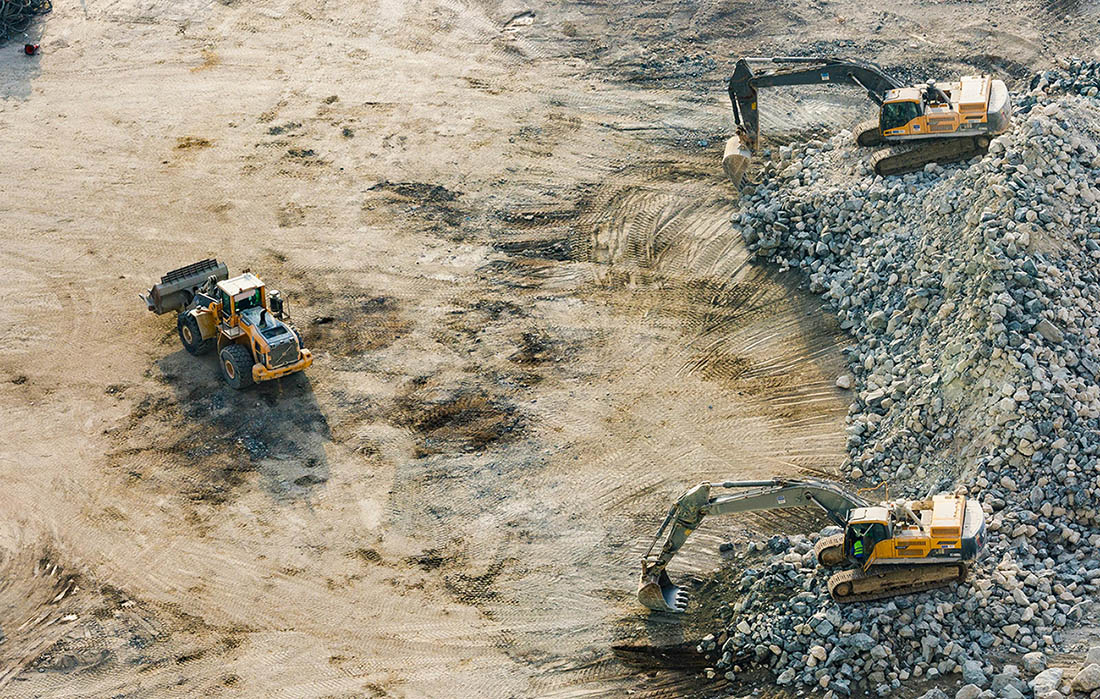
After three years of research on next-generation communication technologies in construction work, the Forschungsfeld Lausitz project, or the 5G FoLa project, came to a close. The results were promising, demonstrating the potential of joined use of 5G and wireless mesh networks for teleoperated construction cases.
Meshmerize is a mobile ad-hoc network that aims to deliver both industry-grade and commercial-level networking solutions for agile and dynamic environments. Meshmerize offers a reliable wireless mesh networking platform for diverse use cases like automated warehouses for Industry 4.0 and mobile robotics.
For these use cases, traditional cellular network coverage may in some cases find it a bit difficult to completely fulfill the required quality of service. In the project, Meshmerize was able to secure a continuous connection through a secondary mesh network. The additional link helped out the primary 5G link which was having a hard time keeping a stable connection in the assigned environment.
About 5G FoLa
The project’s main focus was to investigate communication technologies for the field of teleoperated construction. The research was conducted by using 5G and wireless mesh networks for teleoperation in construction sites. The goal was to see which cutting-edge tech works best in a real-world application.
Assessing wireless mesh networks as a reliable communication system for teleoperation was set as one of the project objectives. Meshmerize provided the project with both the hardware and software required to build the mesh network. Furthermore, we optimized the network to support teleoperation research.
Meshmerize goals
Meshmerize’s goal was to investigate how mesh networks could be integrated into the 5G infrastructure. Additionally, to study the reliability and latency of communication links. To achieve this, we equipped nodes with both Meshmerize and 5G interfaces. Basically, two interfaces allowed the nodes to communicate simultaneously through the mesh and cellular networks.
This seamless integration of the cellular connection was visible to the mesh nodes. The additional path was tasked to improve the efficiency and reliability of the network. In this way, Meshmerize succeeded in establishing an innovative mesh protocol that delivered low latency in wireless networking.
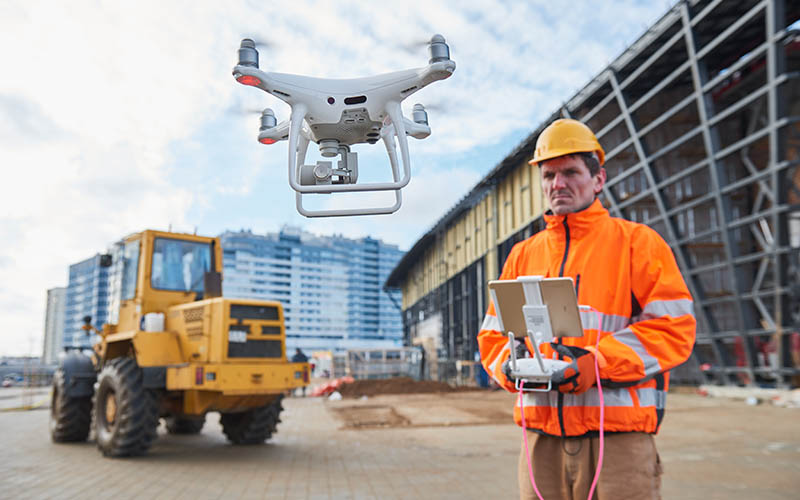
Scenario 1: Drones helping construction machinery teleoperation
A driverless excavator needs to lift and put three pipes to target locations on the construction site. The Base station (BS) and the machine are connected through a 5G link. As long as the excavator stays near the BS, no remote control issues appear.
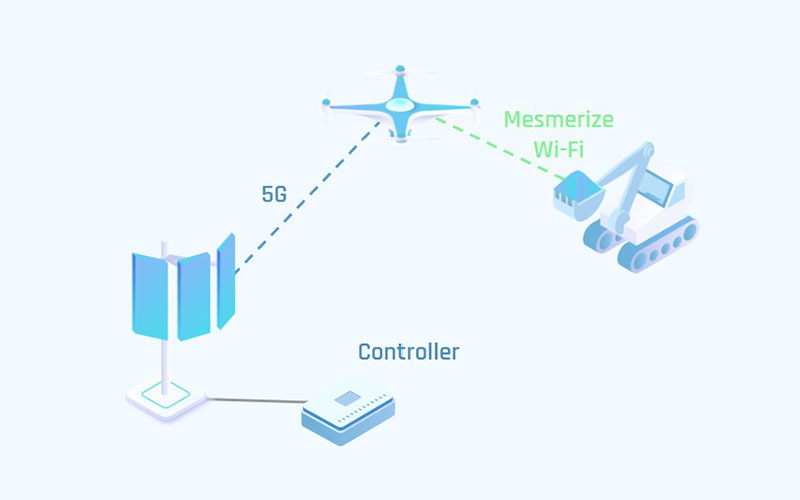
At a larger distance, the quality of the BS link starts to drop, making the communication link unstable. A shaky link can cause problems ranging from simple video distortions to control issues that can potentially lead to crashes.
If there are radio shadows, a complete loss of connectivity can occur. These areas are rather unpredictable on a construction site as the environment is constantly changing. To solve this issue, a drone providing an additional relay link is deployed. The drone ensures a steady connection to the excavator. This is how a secondary mesh network is formed between the BS, drone, and excavator. This network can be extended with additional nodes, providing even more coverage.
Meshmertize multi-path protocol enables the utilization of both BS and drone links at the same time. This creates a smart redundancy by providing a stable connection over unstable links.
Scenario 2: Synchronized Drones for teleoperated construction tasks
Multiple drones need to form a swarm to collaboratively pick up and move a heavy item. They require a reliable local network to disseminate sensor data and synchronize their control data. As the environment on the construction site constantly changes, it poses a challenge for the primary 5G connection to provide connectivity for certain areas covered by obstacles.
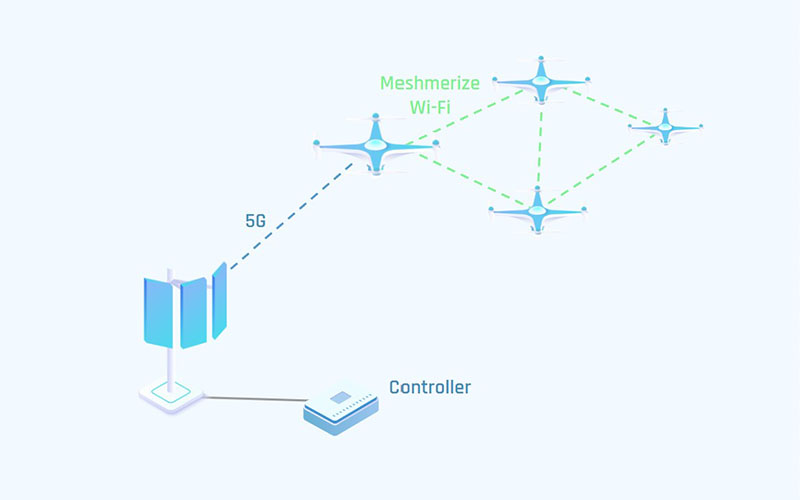
To solve this issue a set of drones forms a secondary mesh network. The secondary link ensures constant connectivity between the machine and the operator in cases when the primary 5G link struggles to maintain a connection.
Each drone is connected to the BS with an individual cellular link. They are also connected via a wireless mesh network. The movement of the drones is controlled by a node that is reachable through the cellular network. To synchronize their movements, the control messages need to be received by the drones simultaneously.
The control messages are sent to each drone at the same time. As soon as the drone receives a control message, it can broadcast the message to all other drones of the swarm through the mesh network. This way, only one drone in the mesh needs to be connected with the 5G link for all the drones to be able to get the control message.
The secondary link secures the stable connection for teleoperated construction
In both of the given scenarios, the conclusions were concordant. 5G FoLa results indicate that 5G cellular alone can have a hard time dealing with the challenges of reliability, low latency, and stability for future automated use cases. This includes drones, driverless transports for Industry 4.0, IoT, mobile devices, etc.
Meshmerize proposed a simple system model to study how mesh networks can help maintain a good connection in various teleoperated construction tasks. As a result, the time disperse control messages received from a remote server was reduced. The results we got are promising: both the analytical approach, as well as with a discrete-event simulator provided matching results.
Overall, the results of the 5G FoLa project demonstrate the potential of using Meshmerize and 5G technology to improve communication in teleoperated construction work. This technology can altogether help to increase safety, efficiency, and reliability on construction sites, paving the way for more advanced applications in the future.
Above all, the results of 5G FoLa bring great satisfaction about what Meshmerize can do. The field of construction is just an example out of numerous use cases for our software.
We are proud to have collaborated with the Vodafone chair at the TU Dresden as the key partner in the project.
Meshmerize is a startup based in Dresden, Germany that provides the ultimate mesh network software to an array of industries. The full potential of Meshmerize is yet to be seen. We would like to hear your thoughts – let us know what you think at [email protected]








